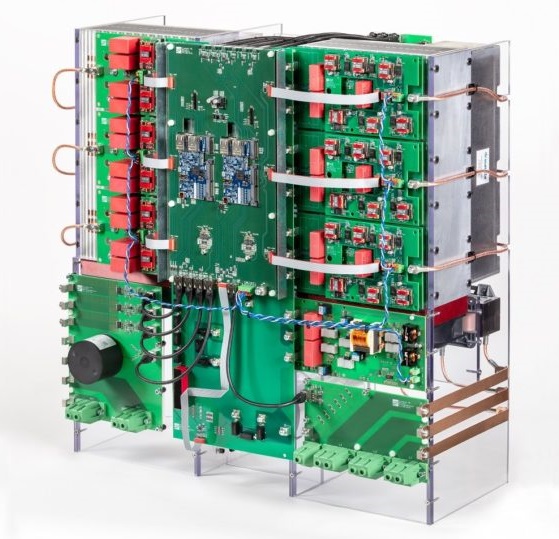
Researchers at Germany’s Fraunhofer Institution for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) have launched a new medium-voltage string inverter aimed at large-scale power plants.
The research body claimed the concept is a world-first for string inverters, using silicon carbide semiconductors to enable output voltage to be increased to 1,500V at 250kVA and potentially paving the way for significant cost savings on system components such as cables.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
In a statement about the launch, Fraunhofer ISE said: “Modern PV string inverters have an output voltage of between 400VAC and 800VAC. Although the output of power plants is steadily growing, voltage has not yet been increased. There are two reasons for this: first, building a highly efficient and compact inverter based on silicon semiconductors is a challenge. Second, there are currently no PV-specific standards that cover only the low-voltage range (max. 1,500Vdc/1,000Vac).”
Under the so-called MS LeiKra project, funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK), Fraunhofer ISE, in collaboration with Siemens and Sumida, said it had developed an inverter that enables the output voltage to be increased to the medium-voltage range (1,500V) at 250 kVA.
It said that central to this achievement is the use of silicon carbide semiconductors, which have a higher blocking voltage. The inverter also employs a more efficient cooling concept using heat pipes, which reduces the amount of aluminium required.
Lower system costs

Increasing the voltage also helps reduce the use of other resources, particularly copper. According to Fraunhofer ISE, at a typical output voltage of 800Vac, a 250kVA string inverter requires cables with a cross section of 120mm2; at the higher voltage that can be reduced to 35mm2, cutting copper use by up to 700 kilograms per kilometre of cable, according to Fraunhofer ISE.
“Our resource analyses show that in the medium term, the electrificiation of the energy system will lead to copper becoming scarce. Increasing the voltage allows us to save valuable resources,” said Fraunhofer ISE director Andreas Bett.
The project team has successfully connected the new inverter to the medium-voltage grid and is now seeking solar farm developers and grid operators to test the new concept in the field.
Alongside developing the new technology, the project team has begun working on new PV-specific standards for the medium voltage. Current standards only cover the lower-voltage range.






